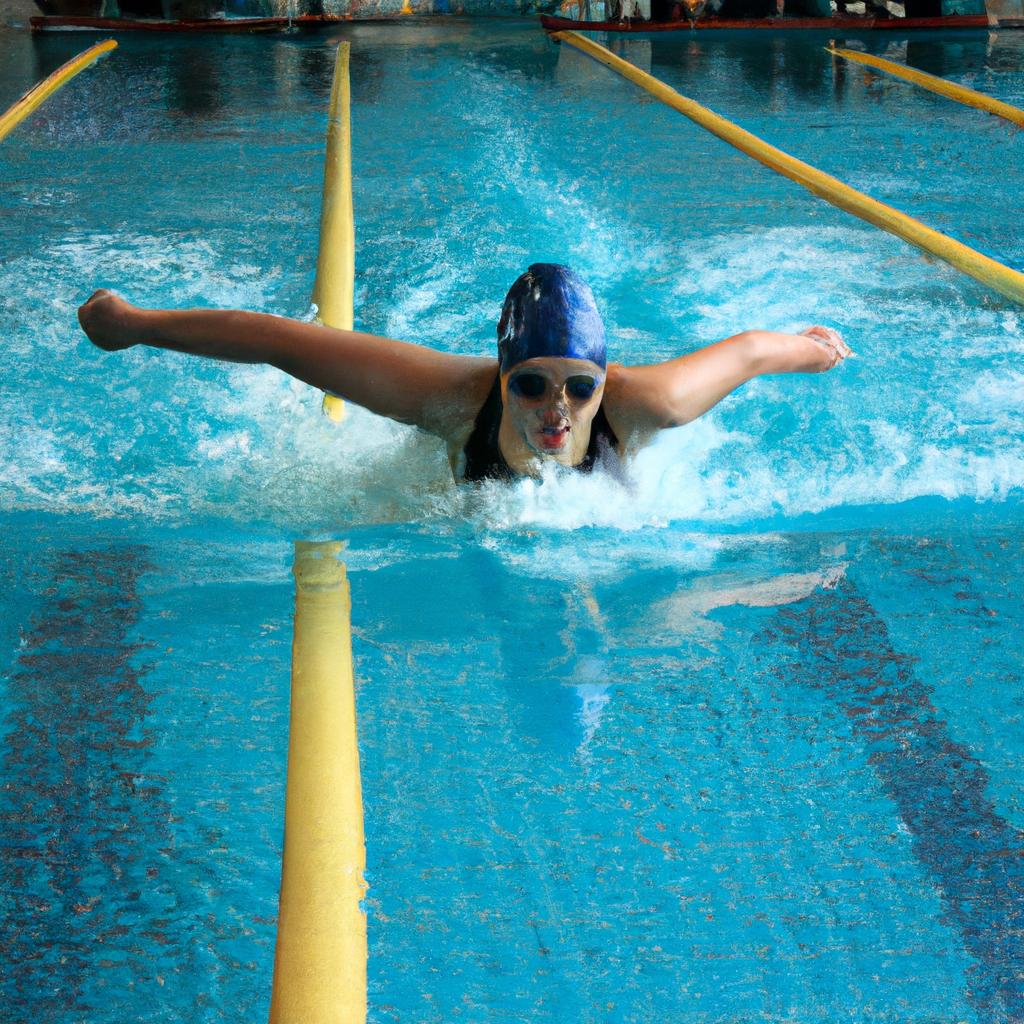
Swimming is a widely recognized and practiced sport that has been incorporated into various games and sports throughout history. Its versatility allows for its inclusion in diverse contexts, ranging from Olympic competitions to recreational activities at the local pool. The aim of this article is to provide readers with an ultimate guide on swimming in games and sports. By exploring different aspects such as techniques, strategies, equipment, and rules, this comprehensive guide seeks to enhance the understanding and appreciation of swimming as it pertains to competitive events and leisurely pastimes.
To illustrate the significance of swimming in games and sports, consider the case study of Michael Phelps, one of the most successful swimmers in history. Throughout his career, Phelps demonstrated exceptional skill and dominance across multiple disciplines within swimming, earning him numerous accolades including 23 Olympic gold medals. His achievements not only solidified his status as a legendary athlete but also showcased how integral swimming can be within the realm of competitive sports. This example serves as a compelling testament to the importance of mastering swimming techniques and harnessing their potential within various game formats.
Within this article’s exploration of swimming in games and sports, readers will gain insights into essential elements such as stroke mechanics, breathing techniques, starts and turns, training methods, mental preparation strategies, as well as the rules and regulations governing swimming competitions. Understanding stroke mechanics, including freestyle, backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly, is crucial for optimizing speed and efficiency in the water. Readers will learn about proper body positioning, arm movements, leg kicks, and timing to execute each stroke effectively.
Breathing techniques play a vital role in maintaining stamina during long-distance swims or intense races. This guide will cover different methods of breathing coordination with each stroke and provide tips on improving lung capacity and breath control.
Starts and turns are critical components of competitive swimming as they can make a significant difference in race outcomes. Readers can expect to gain insights into dive techniques, push-offs from walls, streamline positions, and flip turns that contribute to reducing drag and maximizing speed during transitions.
Training methods tailored specifically for swimming will be explored in this guide. From endurance training to interval workouts, readers will learn how to structure their training sessions effectively to improve strength, speed, and overall performance in the water.
Mental preparation strategies are equally important in swimming as they help athletes maintain focus, manage pre-race nerves, set goals, visualize success, and develop mental toughness. This article will delve into various psychological techniques that swimmers can employ to enhance their mindset before competitions.
Lastly, readers will familiarize themselves with the rules and regulations governing swimming events at various levels of competition. Understanding these guidelines is essential not only for fair gameplay but also for ensuring safety in the water.
In conclusion, whether you’re an aspiring competitive swimmer or someone who enjoys swimming as a recreational activity or fitness workout, this ultimate guide on Swimming in Games and sports aims to equip you with comprehensive knowledge on techniques,
strategies,equipment,and rules that can help you excel in the pool. By delving into all aspects of swimming within different contexts,
this guide seeks to ignite your passion for the sport while providing you with valuable insights that can elevate your skills and enjoyment of swimming as a game and sport.
Different Styles of Swimming
Imagine yourself standing on the edge of a pool, ready to dive in and start swimming. As you prepare for your first stroke, have you ever wondered about the different styles of swimming? Understanding these various techniques can greatly enhance your performance in both recreational games and competitive sports. In this section, we will explore three commonly used swimming styles: freestyle, breaststroke, and butterfly.
Let’s begin with freestyle, also known as front crawl. This style is highly popular due to its efficiency and speed. Swimmers execute alternating arm movements while kicking their legs simultaneously; this propels them forward through the water. Freestyle allows for maximum agility and freedom of movement, making it an ideal choice for long-distance events such as open water races or triathlons.
Next up is breaststroke, characterized by its unique frog-like motion. Swimmers perform symmetrical arm strokes accompanied by simultaneous leg kicks that resemble a frog’s kick. This style emphasizes precision and coordination between upper and lower body movements. Breaststroke provides swimmers with excellent control over their pace, making it suitable for endurance-focused competitions where maintaining a steady rhythm is crucial.
Another captivating style that demands strength and technique is the butterfly stroke. Known for its intense undulating motions resembling those of a butterfly’s wings, this style requires synchronous arm pulls accompanied by dolphin-like leg kicks. The butterfly stroke demands considerable upper body power and core stability due to the continuous undulation performed throughout each lap. It is often favored by athletes competing in short-distance events like sprints or relays.
- Freestyle: Glide effortlessly through the water.
- Breaststroke: Embrace tranquility as you move gracefully.
- Butterfly: Experience exhilaration with powerful strokes.
- Different strokes offer unique challenges and rewards.
Additionally, let us present a table showcasing some key features of each swimming style:
| Style | Arm Movements | Leg Kicks | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freestyle | Alternating | Simultaneous | Easy |
| Breaststroke | Symmetrical | Synchronized frog kick | Moderate |
| Butterfly | Synchronous dolphin-like movement | Dolphin kick with both legs simultaneously | Difficult |
By understanding the characteristics and techniques associated with each style, swimmers can choose the most suitable one for their specific goals and preferences.
In transitioning to our next section on “Swimming Strokes in Competitive Events,” it is essential to note that these three styles form the foundation upon which competitive swimming strokes are built. Each stroke offers its own set of advantages and challenges, paving the way for exciting races and record-breaking performances.
Swimming Strokes in Competitive Events
In the previous section, we explored the various styles of swimming and how they differ from one another. Now let’s delve deeper into the specific swimming strokes used in competitive events.
Imagine a scenario where two swimmers are preparing for an important race. Swimmer A has been practicing freestyle diligently, while Swimmer B prefers butterfly stroke. As they step onto the starting blocks, their chosen swimming styles will greatly influence their performance and ultimately determine who emerges victorious.
To better understand the nuances of different swimming strokes, let’s examine four key aspects that differentiate them:
- Technique: Each swimming stroke requires a distinct set of movements and body positions. For example, breaststroke involves simultaneous arm movements followed by a powerful leg kick, whereas backstroke relies on alternating arm motions with a fluttering leg action.
- Speed: The speed at which each stroke can be executed varies significantly. While butterfly stroke demands tremendous upper body strength and coordination, freestyle offers greater efficiency due to its streamlined technique.
- Energy expenditure: Different strokes require varying amounts of energy expenditure. Breaststroke is known for being more relaxed and energy-efficient compared to butterfly, which places intense strain on both muscles and cardiovascular endurance.
- Muscle engagement: Depending on the stroke chosen, certain muscle groups are engaged differently or more intensely than others. Backstroke primarily targets the back muscles and core stability, while butterfly activates the chest, shoulders, and arms to generate maximum propulsion.
| Stroke | Technique | Speed | Energy Expenditure | Primary Muscles Engaged |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freestyle | Alternating arm pulls | Fast | Moderate | Core (abdominals) |
| Butterfly | Simultaneous arm movements | Very fast | High | Chest, shoulders, arms |
| Breaststroke | Synchronized arm and leg moves | Moderate | Low | Legs (quadriceps) |
| Backstroke | Alternating arm pulls | Moderate | Moderate | Back muscles |
In conclusion, understanding the different swimming strokes is crucial for both swimmers and spectators alike. It allows us to appreciate the technical skills required in each stroke and recognize the strengths and weaknesses of various athletes.
Now let’s move on to discussing “The Technique of Swimming on the Back” without delay.
The Technique of Swimming on the Back
Section H2: The Technique of Swimming on the Back
Imagine a scenario where an aspiring swimmer decides to participate in their first backstroke race. With excitement and nervousness, they step onto the pool deck, ready to showcase their skills. As they dive into the water and begin swimming on their back, it becomes clear that there is much more to this technique than meets the eye.
Swimming on the back requires a unique set of skills and body positioning. To effectively execute this stroke, swimmers must focus on maintaining proper body alignment. This means keeping the head still and aligned with the spine while engaging core muscles for stability. Additionally, a relaxed leg kick propels them through the water, alternating between flexed ankles and pointed toes.
To further understand the intricacies of swimming on your back, consider these key points:
- Body Positioning: It is crucial to maintain a streamlined position by extending arms overhead with palms facing upwards. The shoulders should be rolled slightly inward to reduce drag.
- Arm Movement: Swimmers initiate each arm stroke by pressing down with their palm towards their hip before pushing backward in a semi-circular motion. As one arm recovers above their head, the other begins its underwater pull.
- Breathing Technique: Unlike other strokes, breathing during backstroke involves rotating only the head while keeping most of the body facing upward. By doing so, swimmers can take quick breaths without disrupting their rhythm.
Table – Common Mistakes in Backstroke Technique:
| Mistake | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Overarching Lower Back | Excessive arching of lower back leads to poor body alignment | Increased resistance slows down forward movement |
| Insufficient Leg Kick | Weak or uncoordinated kicks result in reduced propulsion | Slower speed and difficulty maintaining momentum |
| Incorrect Arm Entry | Entering hand too far behind shoulder causes loss of power | Weaker pull and decreased forward movement |
| Inefficient Arm Recovery | Failing to fully extend arm above water increases drag | Slows down overall stroke tempo |
By honing their technique and avoiding these common mistakes, swimmers can greatly improve their performance in backstroke events. The mastery of this stroke requires patience, practice, and a keen eye for proper body alignment.
Understanding the intricacies of swimming on your back sets the foundation for exploring another popular swimming stroke – the breaststroke. With its unique undulating motion and technical requirements, mastering this technique is essential for any swimmer seeking to excel in competitive events.
The Technique of Swimming with a Breaststroke
Swimming on the back is a popular technique utilized in both games and sports. This style of swimming offers its own unique challenges and advantages, making it essential for swimmers to master. To illustrate the significance of this technique, let’s consider the case study of Sarah, an aspiring swimmer who struggled with her backstroke initially but eventually excelled through consistent practice.
One key aspect of swimming on the back is maintaining proper body position in the water. The swimmer lies flat on their back, with their face directed upwards towards the sky or ceiling. This position allows for better balance and minimizes drag as compared to other strokes. By keeping her head still and aligned with her spine, Sarah was able to maintain stability while moving efficiently through the water.
To further enhance performance when swimming on the back, swimmers must focus on specific techniques:
- Arm Movement: A coordinated movement involving pushing one arm up out of the water while simultaneously pulling down with the other arm helps propel the swimmer forward.
- Leg Action: An alternating flutter kick provides propulsion by generating force against the resistance of water.
- Body Rotation: Slight rotation from side to side aids in minimizing drag and increasing power during each stroke cycle.
- Breathing Technique: Proper breathing involves exhaling underwater and inhaling quickly once above water without interrupting coordination between arms and legs.
These techniques can be challenging to grasp at first, but dedication and regular practice yield significant improvements over time. As demonstrated by Sarah’s progress, consistency is key when mastering any swimming technique.
In summary, swimming on the back requires careful attention to body positioning along with precise execution of arm movements, leg action, body rotation, and breathing technique. With practice and perseverance, even beginners like Sarah can overcome initial difficulties and become proficient in this highly valued skill.
Moving forward into our next section about “The Technique of Swimming with a Butterfly Stroke,” we will explore another dynamic swimming technique that demands strength, coordination, and endurance.
The Technique of Swimming with a Butterfly Stroke
From mastering the breaststroke technique, let’s move on to exploring another popular swimming stroke: the butterfly stroke. Imagine yourself gliding through the water like a graceful dolphin, effortlessly propelling your body forward with powerful and synchronized movements. In this section, we will delve into the intricate details of executing the butterfly stroke effectively.
To start off, it is essential to understand the key components of the butterfly stroke:
-
Arm Movement:
- Begin by extending both arms simultaneously out in front of you.
- Pull your arms back towards your chest as if drawing an imaginary circle underwater.
- As your hands reach near your hips, quickly recover them above the surface and repeat the motion.
-
Leg Action:
- Engage your legs in a rhythmic up-and-down kicking motion.
- Keep your knees slightly bent while kicking from your hips.
- Maintain good body alignment throughout, ensuring that your legs are fully extended during each kick.
-
Breathing Technique:
- Unlike other strokes where breathing can be continuous, in butterfly it is more controlled due to its demanding nature.
- Take a breath at every second or third arm recovery above water to avoid compromising speed and efficiency.
-
Body Position:
- A proper undulating body movement is crucial for maintaining momentum and reducing drag.
- Coordinate hip movement with arm action to achieve a smooth wave-like motion along the length of your body.
Now let’s take a look at how these elements come together in executing an effective butterfly stroke:
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| Rhythm | Establishing a steady rhythm allows for efficient coordination between all components of the stroke. |
| Timing | Proper timing ensures seamless transitions between various stages of arm movement and leg action. |
| Strength | The power generated from well-coordinated muscle contractions is necessary for achieving propulsion. |
| Endurance | Building endurance is crucial to maintain the intensity and precision required for an extended period. |
Mastering the butterfly stroke requires practice, patience, and a keen eye for detail. By incorporating these key elements into your swimming technique, you can improve your efficiency in the water and enhance your overall performance.
Transitioning fluidly from the butterfly stroke, we now turn our attention to another widely recognized swimming style: the Freestyle stroke.
The Technique of Swimming with a Freestyle Stroke
Building on the foundation of mastering the butterfly stroke, let us now delve into another essential swimming technique – the freestyle stroke. By understanding and perfecting this style, swimmers can enhance their speed and efficiency in the water, unlocking new possibilities for success in games and sports.
The freestyle stroke, also known as the front crawl, is widely regarded as one of the fastest swimming techniques used in competitive settings. To illustrate its impact, imagine a hypothetical scenario where two swimmers are racing against each other. Swimmer A possesses exceptional strength but lacks effective technique, while Swimmer B has mastered the art of the freestyle stroke. As they dive into the pool, it becomes evident that Swimmer B’s streamlined body position and rhythmic arm strokes propel them effortlessly through the water, leaving Swimmer A struggling to keep up.
To further grasp the intricacies of this stroke, consider these key elements:
- Body Position: Maintaining a horizontal body position with proper alignment minimizes drag and maximizes propulsion.
- Arm Movement: Employing an alternating high-elbow catch followed by a powerful pull through enhances forward motion.
- Breathing Technique: Proper timing and execution of breaths allow swimmers to maintain an efficient rhythm without sacrificing speed.
- Kick Efficiency: Utilizing a strong flutter kick from hips to toes helps generate additional propulsion.
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Body Position | Horizontal alignment with minimal resistance |
| Arm Movement | High elbow catch followed by forceful pull-through |
| Breathing | Timed inhalation/exhalation for maintaining rhythm |
| Kick Efficiency | Strong flutter kick generating propulsive force from hips to toes |
- Unleash your potential by mastering the freestyle stroke
- Enhance speed and efficiency with proper body positioning
- Optimize power through effective arm movements
- Achieve a balanced breathing technique to maintain rhythm and endurance
As swimmers develop their skills in the freestyle stroke, they can begin exploring the challenges of swimming in medley races. By understanding the intricacies of each technique, athletes can adapt fluidly to different strokes and distances, ultimately enhancing their versatility and competitive edge.
The Technique of Swimming in Medley Races
Having learned about the technique of swimming with a freestyle stroke, let us now delve into the technique of swimming in medley races.
Swimming in medley races requires athletes to display versatility and mastery across multiple strokes. Swimmers must seamlessly transition from one stroke to another as they complete different segments of the race. Take for example, Sarah, an aspiring swimmer who excels at both butterfly and backstroke. In a recent competition, she showcased her skills by swiftly switching between these two strokes during the medley relay event.
To excel in medley races, swimmers must focus on several key aspects:
- Stroke Transitions: Smooth transitions are crucial when changing from one stroke to another. Athletes need to practice coordinating their body movements and timing their breaths effectively while transitioning between each stroke.
- Technique Adaptation: Each swimming stroke has its own unique set of techniques and propulsive actions. To be successful in a medley race, swimmers must adapt their technique according to each stroke’s requirements while maintaining efficiency and speed.
- Underwater Kicks: Utilizing powerful underwater kicks can significantly enhance performance during transitions. Efficient dolphin kicks or flutter kicks beneath the water’s surface help maintain momentum and minimize drag before resurfacing for the next stroke.
- Mental Preparedness: Medley races demand mental fortitude as much as physical prowess. Swimmers should mentally rehearse their strategy, visualize seamless transitions, and remain focused throughout the race.
| Stroke | Distance (m) | Key Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Butterfly | 100 | Rhythmic undulating body motion; strong arm pull |
| Backstroke | 100 | Long steady kick; continuous backward arm movement |
| Breaststroke | 100 | Frog-like leg kick; simultaneous arm pull followed by glide |
| Freestyle | 100 | Continuous alternating arm pulls; rhythmic breathing |
Incorporating this knowledge and diligently practicing these techniques, swimmers can excel in medley races. By mastering stroke transitions, adapting technique, utilizing underwater kicks effectively, and maintaining mental preparedness, athletes maximize their potential for success.
With a solid foundation in the technique of swimming in medley races established, let us now explore the challenges faced by long-distance swimmers
Long-Distance Swimming Challenges
Swimming in Games and Sports: Long-Distance Swimming Challenges
Building upon the technique of swimming in medley races, long-distance swimming challenges provide athletes with an opportunity to test their endurance and mental fortitude. One such example is the annual “Oceanic Challenge,” where swimmers must navigate a treacherous 10-kilometer stretch through open waters. This grueling event demands not only physical strength but also strategic planning and mental resilience.
To succeed in long-distance swimming challenges, athletes must consider several key factors. First and foremost, proper training is essential. Endurance workouts that simulate race conditions can help swimmers prepare for the demanding distances they will face. Additionally, incorporating interval training into their routines allows swimmers to improve speed while maintaining stamina over extended periods.
Successful navigation during long-distance swims requires careful attention to environmental variables. Swimmers must be aware of currents, tides, and potential obstacles along their route. By studying charts and consulting experienced coaches or mentors, athletes can develop effective strategies for tackling these challenges.
Furthermore, nutrition plays a crucial role in sustaining energy levels throughout lengthy competitions. Swimmers need to consume adequate calories before, during, and after events to replenish lost nutrients and maintain hydration levels. A well-balanced diet rich in carbohydrates provides the necessary fuel for sustained performance.
In order to evoke an emotional response from both participants and spectators alike, let us delve into some considerations faced by long-distance swimmers:
- Loneliness: The vast expanse of water can create feelings of isolation as swimmers battle fatigue alone.
- Mental toughness: Overcoming doubt and pushing through physical exhaustion becomes paramount when facing challenging conditions.
- Triumph over adversity: Crossing the finish line after enduring hours of grueling effort creates a profound sense of accomplishment.
- Connection with nature: Immersion in open waters offers an unparalleled connection with the natural world.
Table: Successful Strategies for Long-Distance Swimming Challenges
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Pacing | Maintaining a steady and sustainable rhythm throughout the race. |
| Visualization | Utilizing mental imagery to stay focused and motivated. |
| Positive self-talk | Encouraging oneself through affirmations during moments of struggle. |
| Goal setting | Breaking down the challenge into smaller, achievable milestones. |
As swimmers face these unique challenges head-on, they develop resilience not only in their physical abilities but also in their mental strength. The ability to endure and thrive under such demanding conditions is what sets long-distance swimming apart as an extraordinary feat of human capability.
Transitioning seamlessly into our next section on “Swimming in Open Water Competitions,” athletes who conquer long-distance swimming challenges gain valuable experience that prepares them for the unpredictable nature of open water races.
Swimming in Open Water Competitions
Transitioning from the challenges of long-distance swimming, let us now explore the exhilarating world of open water competitions. Imagine you are a competitive swimmer participating in a thrilling race across a vast lake surrounded by breathtaking landscapes. The diversity and unpredictability of open water environments present unique obstacles that test swimmers’ endurance, adaptability, and strategic thinking.
In these competitions, athletes must contend with various factors beyond their control. The following bullet point list provides an overview of some key aspects to consider when navigating open water:
- Navigational Challenges: Swimmers must rely on their navigational skills to find the most efficient route amidst changing currents and wind patterns.
- Temperature Variations: Open water temperatures can range significantly, affecting both comfort levels and physical performance.
- Wildlife Encounters: Competitors may encounter marine life during races, requiring mental composure and respect for nature.
- Tactical Maneuvering: Athletes need to strategize when drafting behind other swimmers or finding favorable positions in the pack.
To further illustrate the complexities of open water competitions, consider the table below showcasing three prominent events along with their distinct characteristics:
| Event | Location | Distance (in km) | Notable Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| English Channel Swim | England-France | 33.8 | Strong tides and cold waters |
| Rottnest Channel Swim | Australia | 19.7 | Sharks and unpredictable weather conditions |
| Manhattan Island Marathon Swim | New York City | 45 | Busy shipping lanes and challenging tidal currents |
As evident from this table, each event presents its own set of hurdles that demand immense dedication and preparation from participants.
Open water competitions offer an invigorating experience for swimmers seeking adventure outside traditional pool settings. Embracing such challenges requires not only physical strength but also mental tenacity and adaptability.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on “Training for Competitive Swimming,” athletes must develop robust skills and endurance to excel in open water competitions.
Training for Competitive Swimming
Moving on from open water competitions, it is crucial to understand the importance of training when aiming for success in competitive swimming. To illustrate this point, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving an aspiring swimmer named Alex. Despite having natural talent and a love for the sport, Alex quickly realized that without proper training, achieving their goals would be challenging.
Training Methods:
To excel in competitive swimming, athletes like Alex must employ various training methods designed to improve their overall performance. Here are some effective techniques commonly used by swimmers:
-
Interval Training:
- Alternate between periods of high-intensity swims and rest or low-intensity recovery.
- Enhances cardiovascular endurance and speed.
- Example: 10 sets of 100-meter sprints with short breaks in between.
-
Weightlifting:
- Strengthens key muscle groups involved in swimming movements.
- Increases power and allows for better propulsion through the water.
- Example: Squats, deadlifts, and shoulder presses using appropriate weights.
-
Dryland Exercises:
- Complementing pool workouts with exercises done outside the water.
- Improves core strength, flexibility, and body control.
- Example: Planks, lunges, yoga poses focusing on balance and stability.
-
Mental Preparation:
- Developing mental toughness is essential for competitive swimmers.
- Techniques such as visualization and positive self-talk can enhance focus and confidence.
Emotional Impact Table:
The following table showcases the emotional impact that proper training can have on a competitive swimmer like Alex:
| Emotion | Before Proper Training | After Proper Training |
|---|---|---|
| Frustration | High | Reduced |
| Confidence | Low | Heightened |
| Motivation | Inconsistent | Sustained |
| Determination | Wavering | Strengthened |
By incorporating these training methods, swimmers like Alex are better equipped to face the challenges of competitive swimming. In the subsequent section, we will delve into specific swimming techniques suitable for beginners who wish to embark on their own aquatic journey.
Swimming Techniques for Beginners
Transitioning from the rigorous training required for competitive swimming, beginners can gradually develop their skills and proficiency in the water. Let’s explore some fundamental swimming techniques that are essential for beginners to learn and master.
To illustrate these techniques, let’s consider a hypothetical beginner named Sarah who has just started her swimming journey. Sarah initially struggles with buoyancy and coordination but is determined to improve her abilities.
-
Body Position:
- Maintain a horizontal body position by keeping your head aligned with your spine.
- Engage your core muscles to maintain stability and balance in the water.
- Imagine yourself as an arrow gliding smoothly through the pool.
-
Breathing Technique:
- Exhale underwater and inhale when turning your head sideways during each stroke.
- Practice rhythmic breathing patterns to ensure a consistent flow of oxygen.
- Remember to exhale fully before taking another breath.
-
Arm Stroke:
- Extend one arm forward while simultaneously pulling the other arm backward.
- Keep your elbows slightly bent throughout the stroke for increased power.
- Gradually increase your speed and efficiency as you gain more experience.
-
Leg Kick:
- Initiate propulsion by kicking from your hips rather than bending at the knees alone.
- Aim for small, quick kicks with relaxed ankles and pointed toes.
- Maintain a steady rhythm between leg kicks and arm strokes.
By incorporating these techniques into her practice sessions, Sarah begins to see improvements in her overall performance. With perseverance, patience, and guidance from experienced coaches or instructors, beginners like Sarah can steadily progress from basic skills towards more advanced swimming techniques.
Moving on to the next section about “Benefits of Swimming for Physical Fitness,” we will delve into how swimming offers numerous advantages beyond its technical aspects.
Benefits of Swimming for Physical Fitness
Transitioning from the previous section on swimming techniques for beginners, let us now explore the numerous benefits that swimming offers for physical fitness. Imagine a hypothetical scenario where John, an individual seeking to improve his overall health and well-being, decides to incorporate swimming into his exercise routine. By examining the advantages of swimming, we can gain insights into how it positively impacts one’s physical fitness.
Firstly, swimming is a low-impact activity that places minimal stress on joints and muscles. This makes it an ideal choice for individuals with injuries or those who want to prevent them. For example, John had previously experienced knee pain while jogging but found relief in swimming due to its gentle nature. The water’s buoyancy reduces the pressure placed on joints, allowing for a full-body workout without straining vulnerable areas.
Secondly, swimming engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. As opposed to other forms of exercise that predominantly target specific regions of the body, such as weightlifting focusing on upper body strength or cycling engaging primarily lower body muscles, swimming requires coordination and activation of various muscle groups throughout the entire body. This comprehensive workout not only improves muscular strength but also enhances endurance and flexibility.
To further emphasize these benefits:
- Swimming increases cardiovascular endurance by raising heart rate levels.
- It helps maintain healthy lung capacity through controlled breathing techniques.
- Regular swim sessions promote weight loss by burning calories efficiently.
- Swimming aids in improving posture and postural control.
Consider this table highlighting some key aspects of swimming:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Low impact | Minimizes strain on joints and allows people with injuries to engage in exercise |
| Full-body workout | Engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously |
| Cardiovascular | Increases heart rate levels and improves endurance |
| Weight management | Efficient calorie burning contributes to maintaining a healthy weight |
Incorporating swimming into one’s fitness routine provides immense advantages. Whether it is the low-impact nature, full-body workout, cardiovascular benefits, or weight management potential, swimming proves to be an excellent choice for improving physical fitness.
By exploring these benefits of swimming, individuals like John can make informed decisions about incorporating this activity into their lives. So consider adding a splash of aquatic exercise to your routine and experience the many rewards that swimming has to offer.