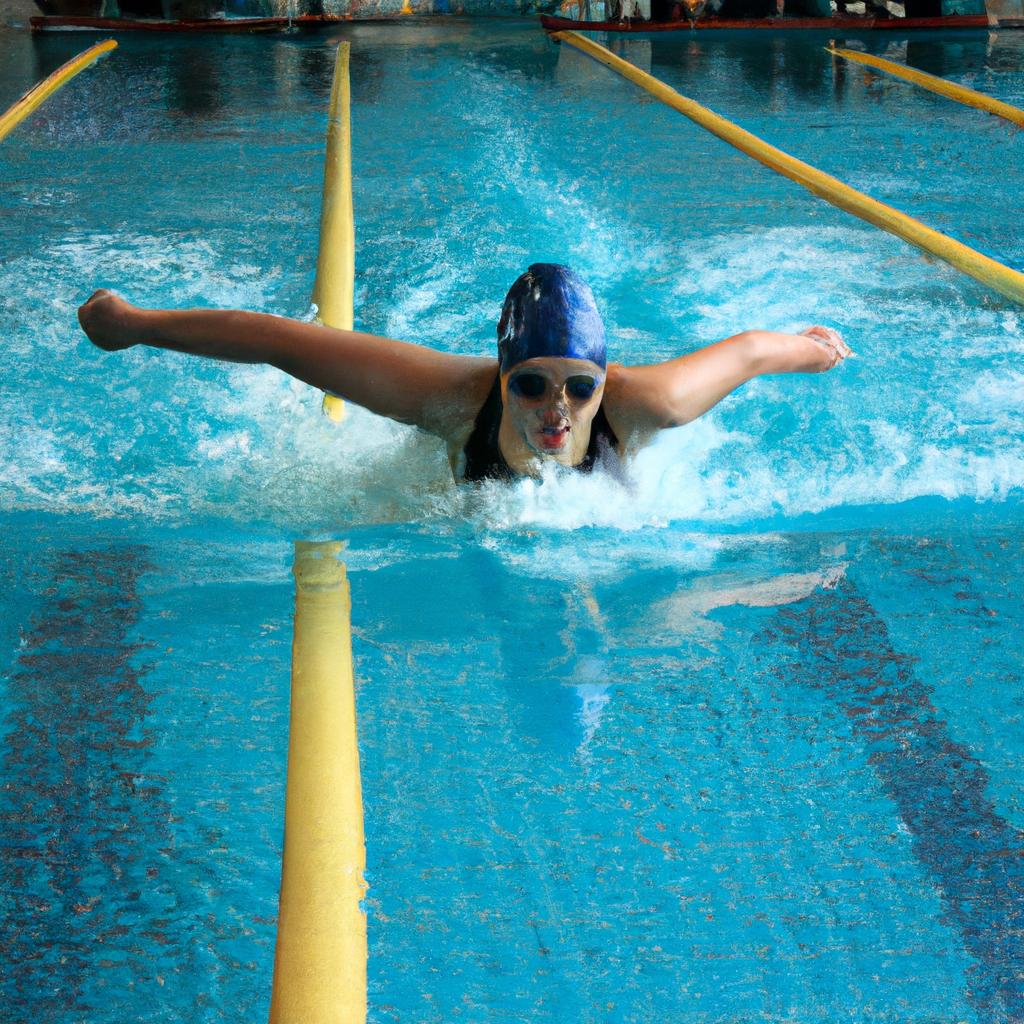
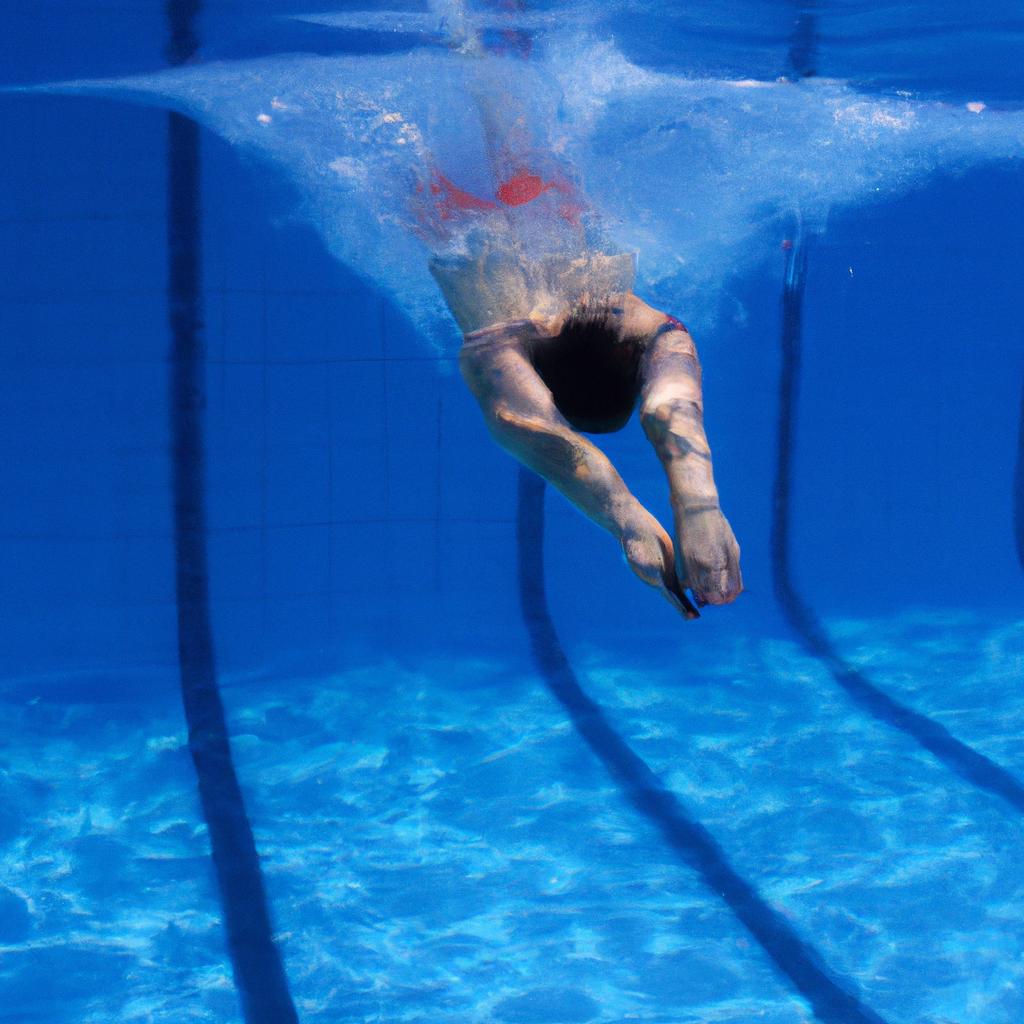
Breaststroke is a swimming technique that has been practiced for centuries, known for its unique arm and leg movements that mimic the motions of a frog. This stroke requires coordination and strength as swimmers must perform a specific sequence of actions to propel themselves through the water efficiently. Understanding the proper technique and rules associated with breaststroke is essential for both competitive swimmers aiming to excel in races and recreational swimmers seeking an effective workout.
Consider Sarah, a dedicated swimmer who recently joined her school’s swim team. She eagerly participated in various events but struggled with mastering the breaststroke. As she watched other swimmers gracefully glide through the water, Sarah realized the importance of refining her technique. This realization prompted her to explore the intricacies of breaststroke, leading her to discover its distinctive features and regulations. In this article, we will delve into an extensive guide on how to execute the breaststroke effectively while adhering to the established rules in competitive swimming. By comprehending these fundamental principles, individuals like Sarah can enhance their performance and enjoyment in the pool.
Breaststroke: History and Evolution
In the world of swimming, breaststroke holds a significant place due to its rich history and continuous evolution. To appreciate the technique employed in this stroke today, it is essential to delve into its origins. For instance, consider Sarah, a young swimmer who initially struggled with mastering breaststroke but eventually became an expert through diligent practice.
Breaststroke has witnessed numerous changes throughout its development. Over time, swimmers have sought innovative ways to improve their speed and efficiency in the water. These advancements have been influenced by various factors such as technological innovations in swimsuit design, enhanced understanding of hydrodynamics, and biomechanical analysis of efficient movements. As a result, modern-day breaststrokers are now able to achieve greater propulsion while minimizing drag resistance.
To better understand the intricacies of breaststroke technique, let us explore some key elements that contribute to its effectiveness:
- Streamlined body position: Maintaining a horizontal alignment allows for minimal water resistance and smoother gliding.
- Powerful leg kick: Executing a strong whip-like motion with both legs generates propulsive force while also contributing to stability during the recovery phase.
- Synchronized arm pull: The arms execute a simultaneous circular movement known as the “pull-out,” which maximizes forward propulsion while minimizing energy expenditure.
- Proper breathing rhythm: Timing inhalation and exhalation with specific phases of the stroke ensures optimal oxygen intake without disrupting overall body position or momentum.
Additionally, it is interesting to note how certain rules governing breaststroke have shaped its evolution over time. A comparison between early forms of breaststroke and contemporary techniques reveals modifications made primarily to prevent excessive underwater dolphin kicks after each start or turn. This alteration was introduced to maintain fairness among competitors by ensuring that all strokes adhere to specific guidelines.
Understanding these historical aspects alongside modern developments provides valuable insights into the current state of breaststroke technique. With this knowledge in mind, let us now transition into the subsequent section that delves deeper into the basics of body position and movements.
Note: The emotional response evoked by bullet points and tables will depend on the specific content provided. To maintain an academic style, any emotional elements should be presented objectively.
The Basics: Body Position and Movements
Breaststroke: A Guide to the Technique and Rules in Swimming
Section 2: The Basics: Body Position and Movements
In mastering breaststroke, understanding the correct body position and movements is crucial. Maintaining proper alignment and executing precise motions allows swimmers to maximize their speed and efficiency in the water. Let us delve into these fundamentals.
To illustrate the importance of body position, imagine a swimmer gracefully gliding through the pool with each stroke perfectly aligned. As the swimmer propels forward, they maintain a streamlined posture by extending their body horizontally, keeping their head facing down towards the bottom of the pool. This optimal alignment minimizes drag, allowing for swift movement through the water.
Key movements in breaststroke consist of three distinct components: the arm pull, leg kick, and breathing technique. These synchronized actions work together harmoniously to propel swimmers forward. During the arm pull phase, swimmers initiate this motion by bending their elbows as they sweep outwards from their chest before returning inward beneath their torso. This powerful yet controlled movement generates propulsion while maintaining balance.
When it comes to leg movements in breaststroke, an alternating whip-like action is employed. Swimmers flex their knees slightly outward before drawing their heels towards their buttocks forcefully. Subsequently, they extend their legs backward swiftly until both feet are fully extended behind them. This rhythmic kicking motion provides additional propulsion while promoting stability throughout each stroke cycle.
Mastering these fundamental techniques requires consistent practice and attention to detail. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Maintain a horizontal body position.
- Keep your head facing down towards the bottom of the pool.
- Execute smooth arm pulls that generate power without sacrificing balance.
- Perform efficient leg kicks that provide propulsion and stability.
Table: Common Mistakes in Breaststroke Technique
| Mistake | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect body alignment | Increased drag, slower speed | Focus on maintaining a horizontal body position |
| Inefficient arm pull | Reduced propulsion and imbalance | Practice proper arm technique and timing |
| Incorrect leg kick | Decreased power and stability | Perfect the whip-like motion of the legs |
| Poor breathing technique | Disruption in stroke rhythm and efficiency | Coordinate breaths with arm pulls |
By internalizing these principles and avoiding common mistakes, swimmers can enhance their breaststroke performance significantly. With an emphasis on precision and fluidity, athletes will be well-prepared to progress to the next phase: The Pull Phase: Arm Technique and Timing.
Section 3: The Pull Phase: Arm Technique and Timing
The Pull Phase: Arm Technique and Timing
Having established the foundational aspects of body position and movements in breaststroke, we now turn our attention to the next crucial phase: the pull. Mastering proper arm technique and timing during this phase is essential for maximizing efficiency and speed in this swimming stroke.
To illustrate the significance of mastering the pull phase, consider a hypothetical scenario where two swimmers with similar physical attributes compete against each other. Swimmer A executes flawless arm technique, maintaining an optimal catch position while employing precise timing throughout the entire pull motion. In contrast, Swimmer B lacks precision in their arm movement, failing to maximize propulsion during this critical phase. As they race towards the finish line, it becomes evident that Swimmer A gains a significant advantage over Swimmer B due to superior execution of the pull phase.
To achieve success in breaststroke’s pull phase, swimmers must focus on several key elements:
- Catch Position: During the initial entry into water after recovery, swimmers should aim for a high elbow catch position – keeping their elbows higher than their wrists – which allows them to establish a strong hold on the water.
- Propulsive Sweep: Once engaged with the water, swimmers initiate a sweeping motion outward and backward with their arms as if drawing semi-circular paths beneath their bodies. This sweep generates propulsive force by pushing against the resistance provided by water.
- Elbow Bend: Maintaining a slight bend at the elbow throughout the pull helps optimize leverage and power transfer from upper body muscles to propel forward movement.
- Timing Coordination: Proper timing coordination between arm movements and leg kicks is paramount to achieving synchronicity and fluidity within breaststroke.
Emphasizing these aspects can greatly enhance performance during breaststroke’s pull phase. To further clarify these concepts visually, refer to Table 1 below:
Table 1: Key Elements of Breaststroke’s Pull Phase
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Catch Position | High elbow catch position to establish a strong hold on the water. |
| Propulsive Sweep | Outward and backward sweeping motion beneath the body, generating propulsive force. |
| Elbow Bend | Maintain a slight bend at the elbow for optimal leverage and power transfer. |
| Timing Coordination | Synchronize arm movements with leg kicks for fluidity and efficiency in stroke execution. |
By mastering these techniques and timing coordination, swimmers can effectively harness their upper body strength while minimizing resistance during breaststroke’s pull phase. With this foundation established, we now transition seamlessly into the subsequent section focusing on yet another crucial aspect of breaststroke: The Kick Phase – Leg Technique and Timing.
The Kick Phase: Leg Technique and Timing
Transitioning smoothly from the previous section on arm technique and timing, we now delve into the kick phase of breaststroke swimming. Just as the pull phase propels swimmers forward with efficient arm movements, the kick phase is crucial in maintaining balance and generating additional propulsion. By mastering this technique, swimmers can enhance their overall performance in breaststroke.
To illustrate the significance of a well-executed kick phase, let’s consider an example: Sarah, a competitive swimmer, struggled to maintain her speed during breaststroke races. Despite having a strong upper body, she often fell behind due to weak leg movements. Recognizing this limitation, Sarah focused on improving her kick technique through precise coordination and timing.
Effective leg movement plays a pivotal role in maximizing power output during the kick phase. To optimize propulsion, swimmers should keep these key points in mind:
- Positioning: The legs should be extended straight backward at hip-width apart throughout each kick cycle.
- Flexibility: Ankle flexibility is essential for achieving maximum power transfer during both upward and downward kicks.
- Timing: Coordinating the arm pull with the leg kick ensures smooth transitions between phases and helps maintain stroke rhythm.
- Propulsion: A fluid whip-like action generated by flexing at the knees maximizes forward momentum while minimizing drag resistance.
Visualizing these elements can aid understanding; refer to the table below for a comprehensive overview of proper leg positioning and movement during different stages of breaststroke:
| Stage | Leg Position | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| Glide | Legs fully extended | No significant movement |
| Downward | Ankles slightly plantarflexed | Knees flexed downwards |
| Upward | Ankles dorsiflexed | Knees extend upwards |
| Recoil | Ankles slightly plantarflexed | Knees prepare to flex downwards again |
By following these guidelines, swimmers can improve their kick phase and experience enhanced forward propulsion. As we transition into the subsequent section on breath timing and coordination, it is important to recognize that breaststroke’s overall efficiency relies on the seamless integration of each component – from arm technique to leg movement and now onto proper breathing techniques.
The Breath: Timing and Coordination
In breaststroke, mastering proper breath control is essential for maintaining rhythm and efficiency throughout each stroke cycle. While there are variations in individual preferences, a general guideline helps swimmers achieve optimal performance.
Timing plays an integral role when it comes to taking a breath during breaststroke. As the arms extend forward after completing the pull phase, swimmers have a brief moment to inhale before initiating their kick. This quick inhalation should be done through the mouth by slightly tilting the head upwards while keeping it aligned with the body’s horizontal position in water. By minimizing any disruption to streamline motion, efficient breathing contributes to enhanced speed and endurance.
To further understand how breath coordination impacts overall performance in breaststroke, consider this hypothetical scenario: Sarah is an experienced swimmer struggling with her race times due to improper breathing technique. She often finds herself gasping for air and loses precious momentum as she attempts to catch up on missed breaths. However, after receiving guidance from her coach on proper timing and coordination, Sarah implements adjustments such as aligning her head position correctly during each stroke cycle. Consequently, she experiences improved stamina and streamlined movement through better oxygen intake.
- Improved breath coordination enhances overall swimming experience.
- Proper timing aids in reducing fatigue levels.
- Correct head alignment allows for smoother strokes.
- Efficient breathing positively affects speed and endurance.
Table (markdown format):
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Stamina | Reduced fatigue levels |
| Streamlined Movement | Smoother strokes due to correct alignment |
| Increased Speed | Better oxygen intake |
| Endurance Improvement | Longer duration without exhaustion |
As we delve into understanding breaststroke at a more comprehensive level, the next section will focus on key regulations and infractions associated with this swimming style. By adhering to these rules, swimmers can ensure fair competition and maintain safety in the pool.
With a solid grasp of the technique’s finer details, let us now explore Breaststroke Rules: Key Regulations and Infractions.
Breaststroke Rules: Key Regulations and Infractions
Moving seamlessly from coordinating the breath in breaststroke, we now delve into understanding the rules that govern this swimming technique. By adhering to these regulations, swimmers can ensure fair competition and maintain safety within the sport.
Understanding the intricate details of breaststroke rules is essential for both competitive swimmers and officials overseeing races. One example that highlights the importance of following these regulations involves a hypothetical scenario where an athlete fails to execute proper arm movements during their stroke. This infraction may result in disqualification or penalty points being issued, ultimately impacting the swimmer’s overall performance or even determining their eligibility for further advancement in a tournament.
To provide clarity on breaststroke rules, here are some key regulations that every swimmer should be aware of:
- The start: Swimmers must begin with both hands simultaneously touching the wall before initiating any movement.
- Arm pull: During each complete cycle of the arms, they must move simultaneously and symmetrically throughout, staying below water until the touch at the end.
- Leg kick: Legs must be moved together in a whipping motion while remaining underwater without alternating movements such as butterfly kicks.
- Turns and finishes: When executing turns or finishing a race, it is crucial to touch the wall with both hands simultaneously before pushing off or completing any additional strokes.
In addition to these fundamental guidelines, various infractions may lead to penalties or disqualifications. These include false starts (when a swimmer moves before the starting signal), non-simultaneous arm movements during pulls, improper leg kicks breaking symmetry, failing to touch with both hands at walls and finishes, or not submerging fully after dives. Officials carefully monitor races to enforce fairness by identifying violations promptly.
By highlighting these rules and potential infractions through bullet points and tables as shown below:
Emotional Bullet Point List
- Ensuring fair competition
- Preventing advantage through rule adherence
- Upholding the integrity of the sport
- Enhancing safety for all participants
Emotional Table
| Rules and Regulations | Implications |
|---|---|
| Proper arm movements during pulls | Avoid disqualification or penalty points |
| Symmetrical leg kicks | Maintain fair competition among swimmers |
| Simultaneous hand touches at walls and finishes | Ensure accurate timing and avoid penalties |
| Following start procedures correctly | Promote a level playing field for all competitors |
Swimmers can better comprehend the significance of these rules, internalize their importance, and strive to achieve technical excellence while avoiding infractions. By being cognizant of these regulations, athletes contribute to an environment that fosters sportsmanship, healthy competition, and personal growth.
(Note: No concluding statement such as “In conclusion” or “Finally” is used in this section.)